SUSE and Bosch: Pioneering Industrial IoT with a Hybrid Cloud Control and Monitoring Architecture
Introduction to Edge and Industrial IoT:
In the era of rapid digital transformation, Edge Computing and the Internet of Things (IoT) stand out as pivotal technologies driving innovation. Edge Computing represents a paradigm shift, processing data close to the source, thus reducing latency and bandwidth use. IoT extends this capability, interlinking physical devices with computing systems, enabling them to send and receive data.
Despite the transformative potential of these technologies, they introduce significant challenges, particularly in the context of Industrial IoT (IIoT). Security is a predominant concern. With an increasing number of devices connecting to the network, the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks escalates. Protecting sensitive industrial data and ensuring the integrity of machine-to-machine communication is paramount.
Scalability is another critical challenge. Industrial systems must be capable of expanding to accommodate growing data volumes and an increasing number of devices, without compromising performance. This scalability must be managed efficiently to support the dynamic and often rapid changes in industrial operations.

Addressing these challenges is essential for any organization looking to harness the benefits of Industrial IoT. Solutions must be robust enough to protect against sophisticated security threats and flexible enough to scale with the ever evolving demands of industrial environments. It is not just about technology implementation, it’s about creating a secure and resilient infrastructure that can grow and adapt as the needs of the industry change.
By understanding and acknowledging these challenges, industries can pave the way for innovative solutions that leverage Edge and IoT technologies to create smarter, safer, and more scalable operations. We’ll delve into how the joint reference architecture by SUSE and Bosch specifically addresses these challenges to provide a solid foundation for modern Industrial IoT solutions.
Interoperability and Open Standards:
The diverse landscape of devices and protocols often results in fragmented systems that are challenging to manage and scale. Open standards emerge as a beacon of hope, providing a common language and set of rules that ensure different systems and devices can understand each other, paving the way for seamless vendor collaboration. The emphasis on open standards ensures that as new devices and technologies emerge, they can be integrated into the existing infrastructure without significant overhauls, thus supporting truly scalable and interoperable Industrial IoT systems.
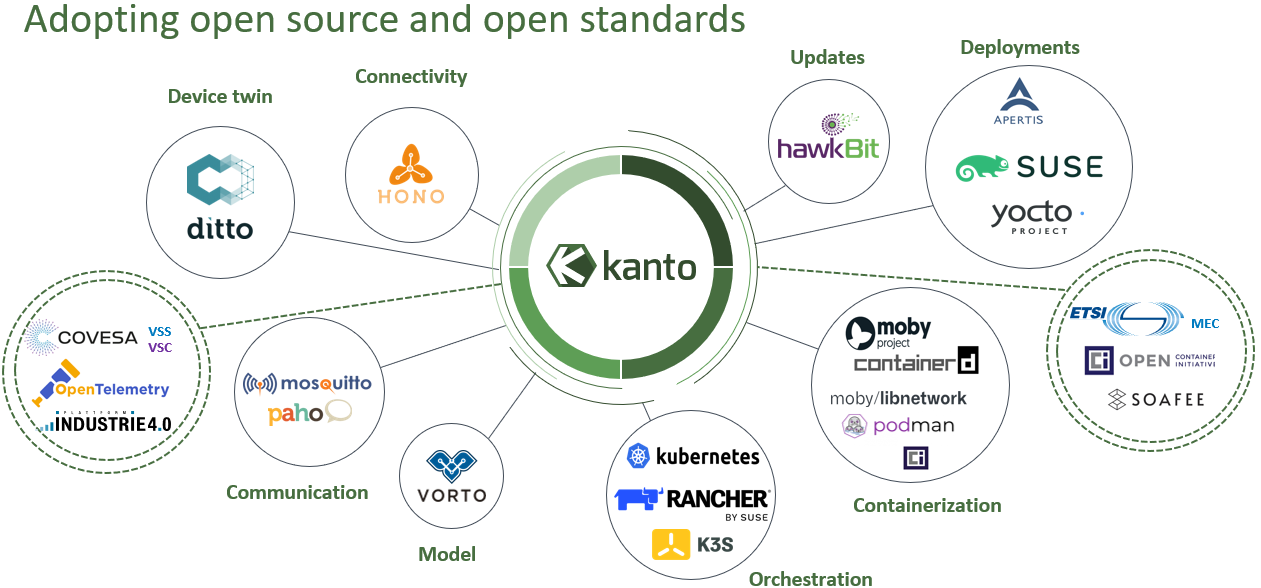
Joint Reference Architecture Overview:
The joint reference architecture from SUSE and Bosch outlines a hybrid-cloud, multi-technology stack designed to control and monitor industrial robots, embodying a fusion of security, automation, and Industrial IoT (IIoT) advancements. It utilizes on-premises and cloud deployment of SLE Micro and Eclipse Kanto, alongside Rancher-managed K3s clusters and Eclipse Ditto. The architecture significantly benefits industrial IoT customers by providing real-time monitoring, control, and enhanced security, thus promoting operational efficiency and smarter decision-making in a manufacturing setup, at scale.

Components and Functions:
- Industrial IoT robot:
- Overview: An advanced Industrial IoT robot, in this scenario Giga Automata’s Animoto Robot, designed for specialized manufacturing applications.
- Function: Executes physical tasks based on instructions received from the on-premises and cloud-based components of the stack.
- Benefits: Provides efficient, automated task execution in a manufacturing environment.
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Micro (SLE Micro):
- Overview: A lightweight, reliable, immutable operating system geared for edge computing environments.
- Function: Hosts both the on-premises part of the stack, providing a stable and secure environment for Eclipse Kanto and the connection to the Industrial IoT robot, as well as the cloud part of the stack, in a cloud provider of your choice, providing a robust, efficient, and secure environment for containerized applications and edge computing.
- Benefits: Ensures enhanced security, stability, and performance in edge environments.
- Rancher-managed K3s clusters on a cloud provider of your choice:
- Overview: Rancher simplifies the deployment and management of Kubernetes clusters, while K3s is the leading lightweight Kubernetes distribution designed for simplicity and low resource consumption.
- Function: Rancher manages the K3s clusters on a cloud provider of your choice, orchestrating containerized services and workloads.
- Benefits: Streamlines management, scaling, and orchestration of containerized applications and services, enhancing operational efficiency.
- Backend Services on a cloud provider of your choice or on-premises:
- Bosch IoT Remote Manager:
- Overview: A component for centralized remote management of devices and gateways.
- Function: Serves as an intermediary for managing and monitoring communication between on-premises and cloud-based components, ensuring seamless and secure data flow and control commands.
- Benefits: Enhances data communication security and management, promoting effective monitoring and control across the architecture.
- Eclipse Ditto:
- Overview: Eclipse Ditto is an open-source platform under the Eclipse Foundation, which facilitates the creation and management of digital twins.
- Function: Establishes a digital twin of the Industrial IoT robot, enabling real-time monitoring and control.
- Benefits: Enhances monitoring, analysis, and control over the robot’s operations, delivering real-time operational insights and control.
- Bosch IoT Remote Manager:
- Eclipse Kanto:
- Overview: An open-source project under the Eclipse Foundation that enables devices for IoT with all essentials like cloud connectivity, digital twins, local communication, container management, and software updates.
- Function: Facilitates the development and deployment of intelligent applications on-premises, enabling robust interaction with the Industrial IoT robot.
- Benefits: Accelerates the development of smart applications, promoting seamless integration between on-premises and cloud components, thereby improving edge devices management.
You can get a sneak peak of the above stack in action in this demo.
Integration and Flow:
- In this scenario, SLE Micro and Eclipse Kanto are deployed on-premises and they interact with the Industrial IoT robot, providing local control and intelligent application management.
- The K3s cluster, managed by Rancher (running on SLE Micro) on a cloud provider of your choice, orchestrates the containerized services and workloads vital for the operation of the entire stack.
- Eclipse Ditto, deployed on a cloud provider of your choice, creates a digital twin of the robot, allowing for real-time monitoring and control from the cloud.
- Bosch IoT Remote Manager facilitates secure and seamless communication between the on-premises and cloud-based components, ensuring efficient, secure, real-time control and monitoring of the Industrial IoT robot.
Real-time Monitoring and Control:
With the setup, operators can monitor the Industrial IoT robot in real time through the digital twin representation on Eclipse Ditto. Any operational data or insights gathered can be analyzed in real time, enabling smarter decision-making and enhanced operational efficiency in the manufacturing setup.
Feedback Loop:
A feedback loop is created whereby data from the Industrial IoT robot can be sent back to the cloud for analysis, and control commands can be sent from the cloud or on-premises components to the robot for executing tasks.
Security and Automation:
Throughout this architecture, security and automation are emphasized to ensure safe, efficient, and automated task execution, fulfilling the overarching aim of promoting operational efficiency and smarter decision-making within a manufacturing setup. The architecture outlines a seamless integration of on-premises and cloud-based technologies, orchestrating a robust, hybrid-cloud solution for real-time control, monitoring, and intelligent interaction with an industrial IoT robot, thereby significantly enhancing the automation capabilities in an industrial environment.
Conclusion:
The SUSE and Bosch joint reference architecture offers a comprehensive solution to the management and scalability challenges in Industrial IoT. By providing tools and platforms that are inherently scalable, secure, and interoperable, this stack ensures that industrial enterprises can not only start small and grow as needed, but also seamlessly integrate diverse technologies and manage them efficiently across a broad operational landscape.
Scalability stands as one of the most significant challenges in the realm of Industrial IoT solutions. As enterprises grow and technology evolves, the need for systems that can easily scale up to accommodate increased loads and scale out to integrate new types of devices and services becomes paramount. This synergy between SUSE’s edge computing expertise and Bosch’s IoT prowess equips industrial organizations with a future-proof infrastructure that can adapt and expand, driving innovation and operational efficiency at scale. By integrating on-premises and cloud-based technologies, it lays down a framework for efficient, secure, real-time operational insights and control, significantly enhancing the automation capabilities in an industrial environment.
To explore how the SUSE and Bosch joint reference architecture can revolutionize your Industrial IoT capabilities, please reach out to the SUSE sales team and the Bosch sales team to discuss your specific needs and how our solutions can be tailored to your enterprise:
https://www.bosch-softwaretechnologies.com/en/locations/
Authors:
 Kristiyan Gostev, Project Lead on the Eclipse Kanto project and Lead Software Engineer at Bosch Digital
Kristiyan Gostev, Project Lead on the Eclipse Kanto project and Lead Software Engineer at Bosch Digital
Kristiyan brings 8 years of experience in software development and delivering high impact projects.
 Andrew Gracey, Lead Product Manager for Cloud Native Edge at SUSE
Andrew Gracey, Lead Product Manager for Cloud Native Edge at SUSE
Passionate about making a positive impact on the world through technical and human process design. Andrew has 9+ years of experience in the tech industry serving in roles requiring fast-paced and creative design, a solid understanding of project’s fit in the market, and project management/expectation management skills.
