How to Install PHP 8 on RHEL 9 | Rocky Linux 9
PHP is a recursive acronym for Hypertext Preprocessor. It is a popular and widely used server-side scripting language used in web development and can even be embedded in HTML pages. Although there are other new scripting languages such as Perl and Ruby, PHP still remains popular and powers some of the most popular websites such as Facebook, WordPress, and MailChimp.
Prerequisites
- Pre-installed RHEL 9 or Rocky Linux 9 or Alma Linux 9
- Sudo user with admin rights
- Internet Connectivity
In this post, we look at how to install PHP 8.2 on RHEL 9 / Rocky Linux 9 / AlmaLinux OS 9.
Step 1) Update System Packages
To get started, log into your server instance and be sure to update installed packages to their latest versions as shown below.
$ sudo dnf update -y
To ensure that all changes have come into effect, restart your server instance.
$ sudo reboot
Step 2) Add the Remi repository
In this tutorial, we will install the latest version of PHP which is PHP 8.2 from the Remi repository. This is a third-party repository that provides the latest versions of PHP and other packages for RHEL-based Linux distributions.
To install Remi, first, you need to install EPEL as a prerequisite. EPEL, short for Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux, is a repository maintained by Fedora which contains additional packages for Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), and RHEL-based distributions such as Alma Linux and Rocky Linux.
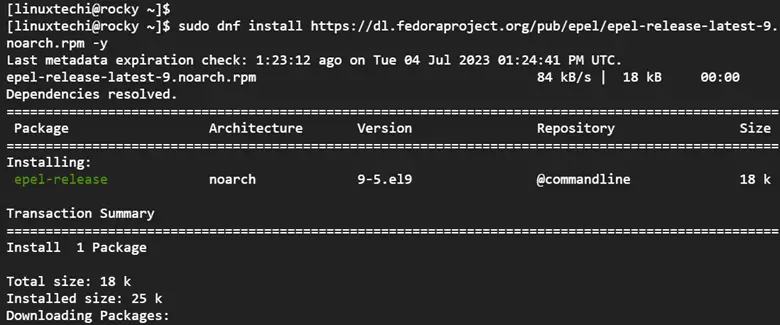
Therefore, install EPEL as shown.
$ sudo dnf -y install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm -y
Once done, confirm that the EPEL repository has been installed.
$ rpm -q epel-release
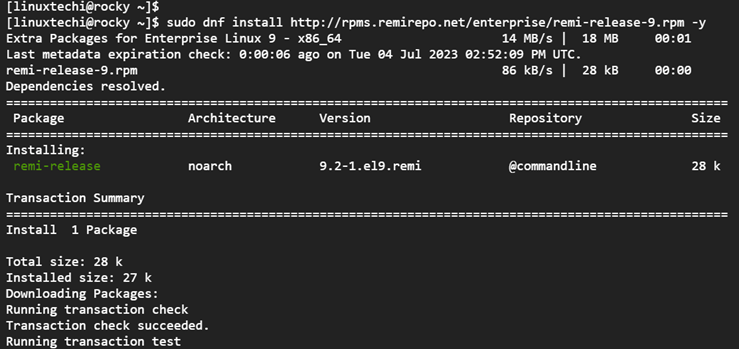
The next step is to add the Remi repository, and to do so, run the command:
$ sudo dnf -y install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-8.rpm -y
You can verify if Remi is installed using the command:
$ rpm -q remi-release
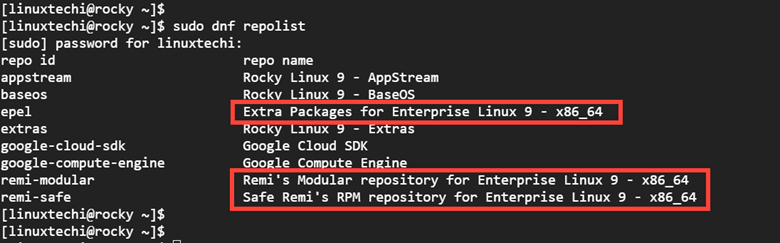
Additionally, you can list configured repositories on your system as follows. Be sure that you can see EPEL and Remi repository entries.
Step 3) Install PHP 8.2 on RHEL 9 / Rocky 9 / AlmaLinux 9
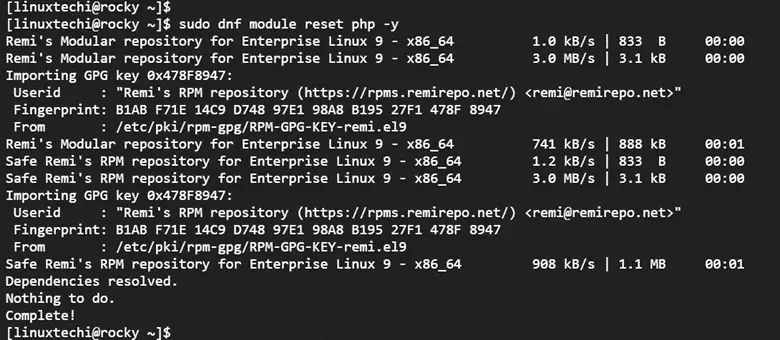
With both repositories installed, the next step is to install PHP 8.2. Before proceeding, reset the default PHP module.
$ sudo dnf module reset php -y
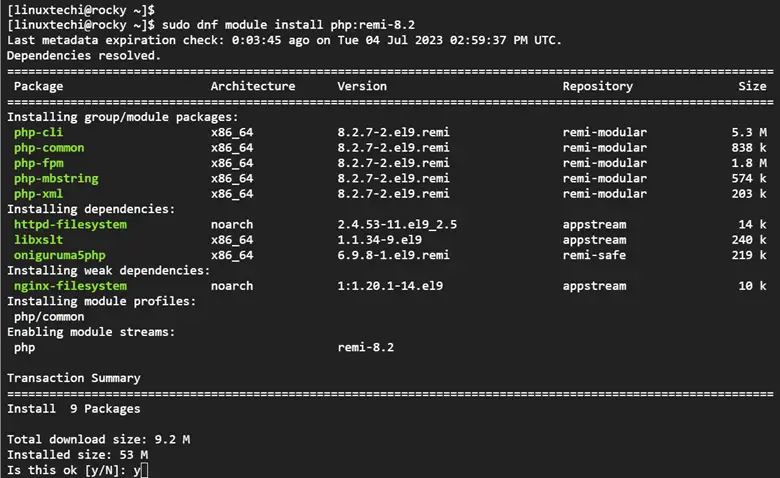
Next, enable the PHP Remi 8.2 module that contains the PHP packages to be installed.
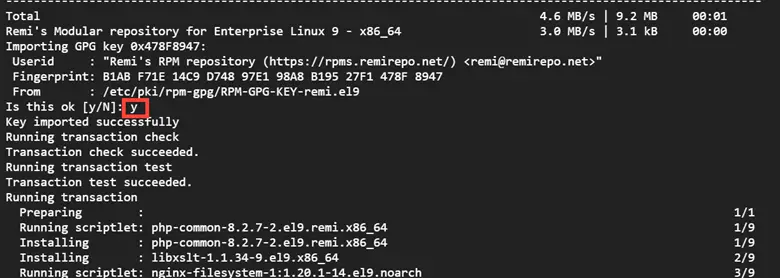
$ sudo dnf module install php:remi-8.2
When prompted, hit ‘Y’ and press ENTER to import the GPG key.
Next, install PHP 8.2 and dependency packages
$ sudo dnf -y install php
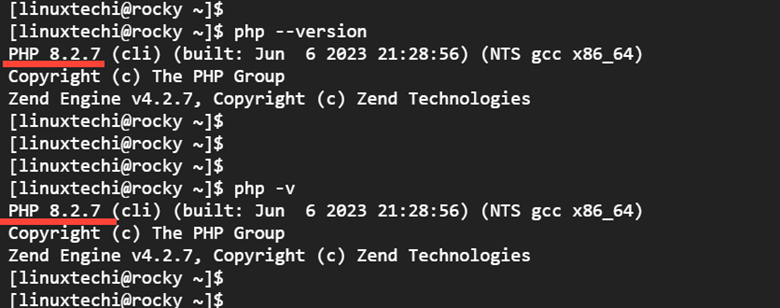
Once installed, confirm the PHP version as shown
$ php --version OR $ php -v
From the output, you can see that we have installed PHP 8.2.7.
Additionally, you can install PHP modules to extend the functionality of PHP. This takes the following syntax:
$ sudo dnf install php-extension_name
If you are installing multiple PHP extensions, you can use the shortened form as shown.
$ sudo dnf install php-{extension1,extension2}
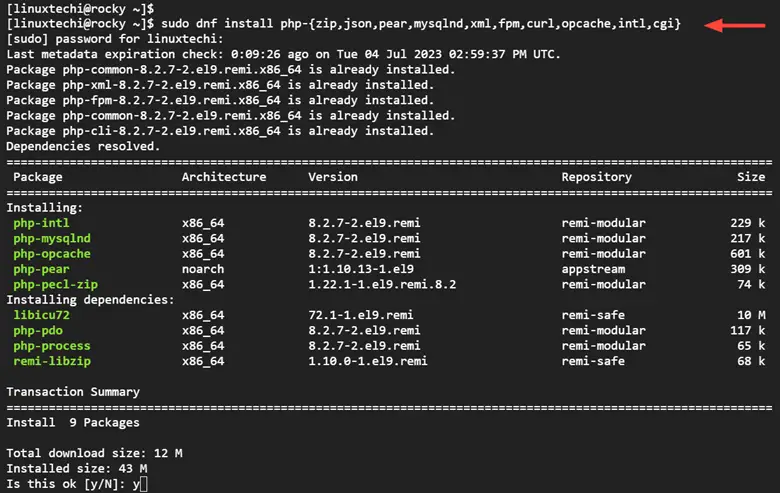
In this example, we are installing a set of PHP extensions as shown.
$ sudo dnf install php-{zip,json,pear,mysqlnd, xml,fpm,curl,opcache,intl,cgi}
When prompted, press ‘y’ and hit ENTER to proceed.
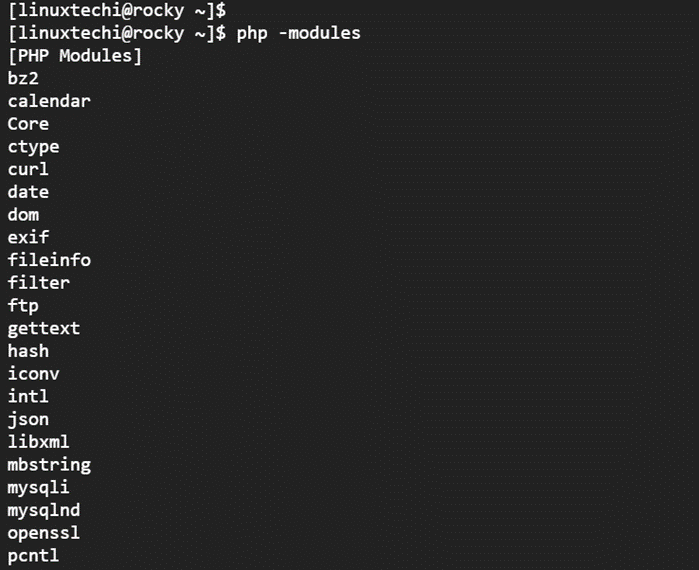
To view all installed modules, run the command:
$ php -modules
Integrating PHP with Apache Web Server
The mod_php module is an Apache module that enables Apache to parse php code and interpret PHP files. When a user requests a PHP page, the web server fetches the requested PHP file, executes the code, and returns HTML content to the client’s web browser. This eliminates the need of having a separate PHP interpreter.
The Apache web server comes with the mod_php module as one of the packages. So you can go ahead and install Apache as shown.
$ sudo dnf install httpd -y
Next, enable the Apache web server service.
$ sudo systemctl enable httpd $ sudo systemctl start httpd
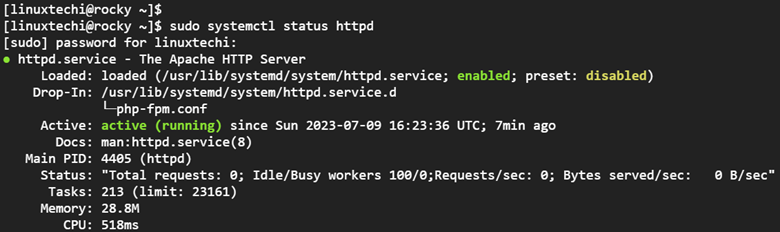
Be sure to confirm that Apache is running.
$ sudo systemctl status httpd
Next, create a sample PHP file in the web root directory.
$ sudo nano /var/www/html/info.php
Add the following code
<?php phpinfo() ?>
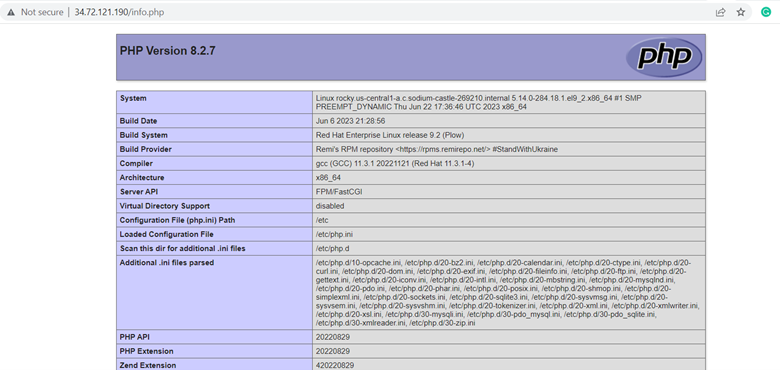
Save the changes and exit the file. To confirm that the web server is ready to serve PHP pages, browse your URL as shown.
http://server-ip/info.php
This displays what you can see below, a confirmation that your web server is able to parse PHP code.
Integrating PHP with Nginx Web Server
When running the Nginx web server, PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) is the recommended way of processing PHP pages. It’s faster than mod_php and other traditional CGI-based avenues. It consumes less computing resources such as CPU and memory compared with other methods. In addition, it allows you to run PHP as a daemon, which can be managed using systemd.
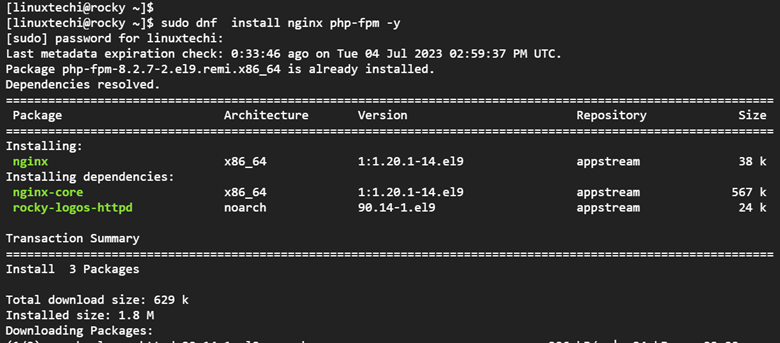
To demonstrate how to use PHP with Nginx, we will install Nginx alongside PHP-FPM as shown.
$ sudo dnf install nginx php-fpm -y
If you have Apache installed, be sure to stop the service since t runs on port 80 which Nginx will use.
$ sudo systemctl stop httpd
Next, enable and start Nginx and PHP-FPM.
$ sudo systemctl enable --now nginx php-fpm
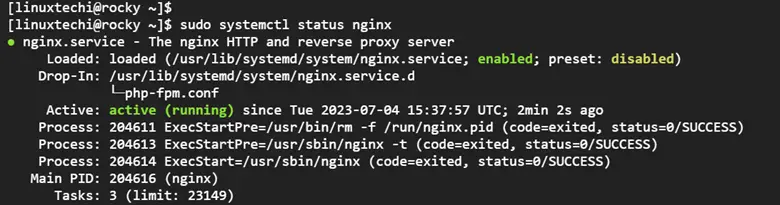
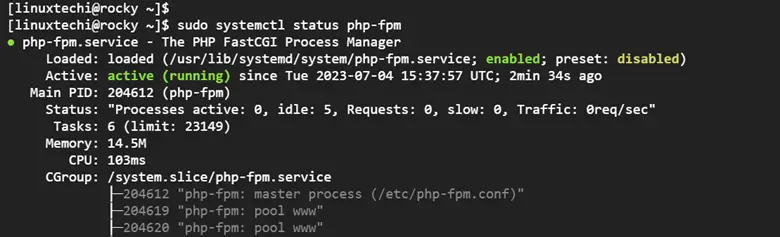
Be sure to confirm that Nginx and PHP-FPM services are running.
$ sudo systemctl status nginx
$ sudo systemctl status php-fpm
Next, edit the www.conf file as shown:
$ sudo vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
Add the following lines.
user = nginx group = nginx listen = /var/run/php-fpm.sock listen.owner = nginx listen.group = nginx listen.mode = 0660
Save and exit the configuration file. Next, we need to configure Nginx to forward requests to PHP-FPM. To accomplish this, access the Nginx main configuration file.
$ sudo vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
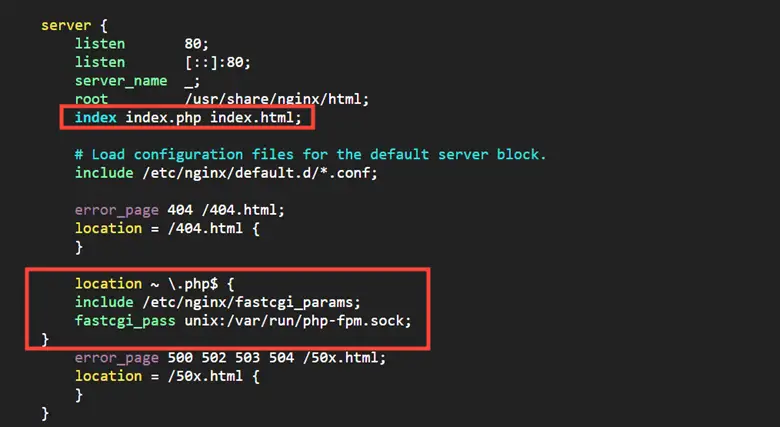
Add the following line under the root directive.
index index.php index.html;
Next, add the following lines to forward requests to PHP-FPM
location ~ .php$ {
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php-fpm.sock;
}
Save the changes and exit the configuration file. To apply the changes made, restart Nginx and PHP-FPM.
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx $ sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
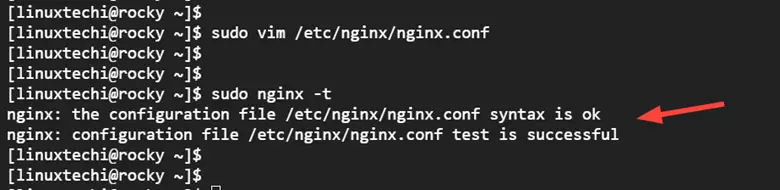
Next, verify if the Nginx configuration is sound
$ sudo nginx -t
Next, we will create a sample info.php file
$ sudo nano /usr/share/nginx/html/info.php
Add the following code
<?php phpinfo() ?>
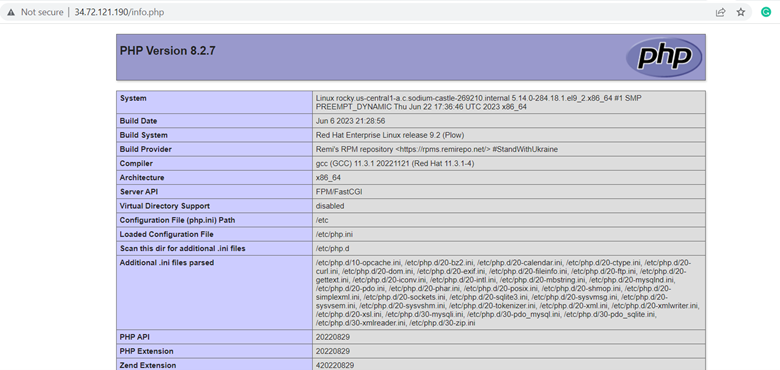
Save the changes and exit the file. To confirm that Nginx is ready to serve PHP pages, once again, browse your URL as shown.
http://server-ip/info.php
Conclusion
In this guide, we have shown you how to install PHP 8.2 on RHEL 9 and RHEL-9-based distros such as Rocky Linux 9 and AlmaLinux 9. We have also demonstrated how you can configure PHP to work with Apache and Nginx web browsers.