Downgrading a Package via apt-get in Ubuntu and Debian
In a situation where a recently upgraded software is causing issues?
While you can always investigate the issue to fix it, at times, going back to the previous working version saves time and effort.
If the new version introduced a bug, you could do nothing on your end, right?
The good thing is that you can easily downgrade an apt package in Ubuntu and Debian.
All you have to do is to use the apt command like this:
sudo apt install package_name=package-version-numberThat seems easy enough but how would you get the exact version number? Which old versions are supported? You can get that detail with:
sudo apt-cache policy package_nameLet me explain all this with a real-life example.
Downgrading apt package
Recently, I was updating the Ubuntu server that hosts It’s FOSS Community forum.
I did the usual apt update && apt upgrade and things went bonkers by the time updates were installed.
Apparently, the latest version of Docker didn’t support the aufs storage driver. To reduce the downtime, I opted to downgrade to the previous Docker version.
Check the currently installed package version
Then check for the available versions that could be installed:
sudo apt-cache policy package_nameIt may throw a huge list or just a small one:
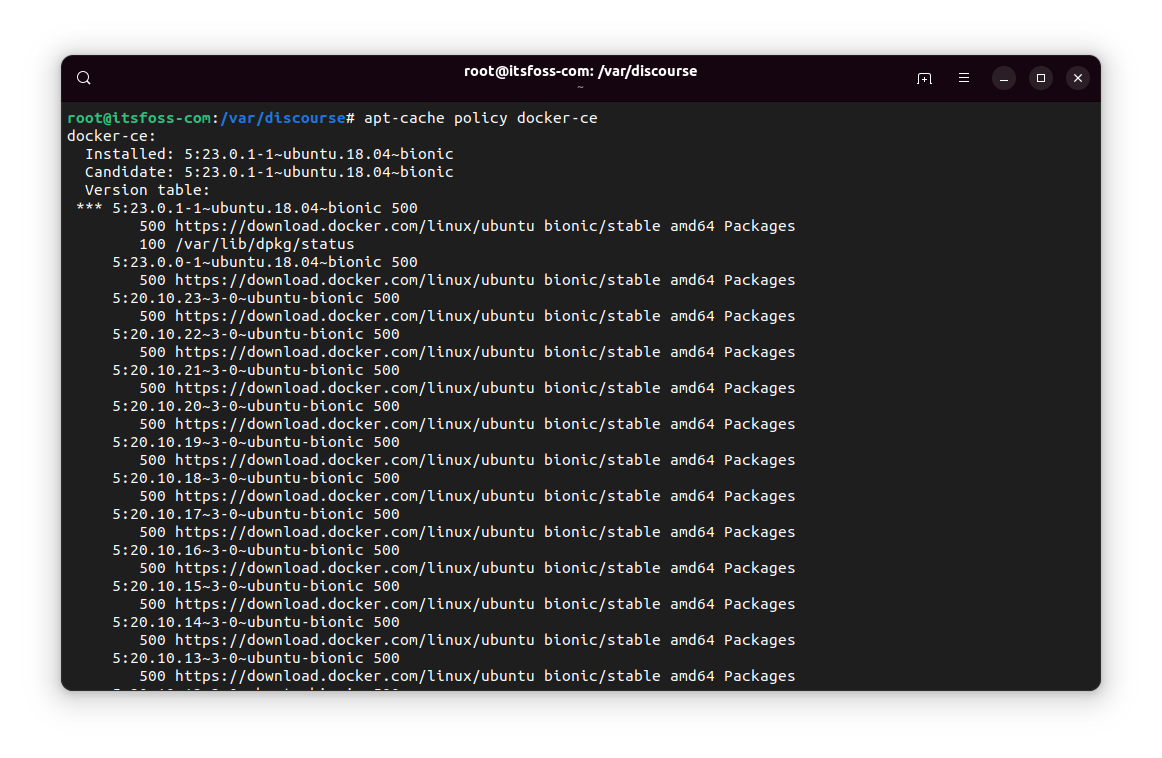
If it shows at least one older version than the current one, you are in luck.
Now, you may think that the version number of a package would be composed of just the numbers. But that may not always be the case.
Basically, you copy the entire stuff before 500 (the priority number).
brave-browser:
Installed: 1.48.158
Candidate: 1.48.164
Version table:
1.48.164 500
500 https://brave-browser-apt-release.s3.brave.com stable/main amd64 Packages
*** 1.48.158 500
500 https://brave-browser-apt-release.s3.brave.com stable/main amd64 Packages
100 /var/lib/dpkg/status
1.47.186 500
500 https://brave-browser-apt-release.s3.brave.com stable/main amd64 Packages
1.47.171 500
500 https://brave-browser-apt-release.s3.brave.com stable/main amd64 Packages
1.46.153 500
Once you have got the package number, use it to downgrade the installed package like this:
sudo apt install package_name=package-version-number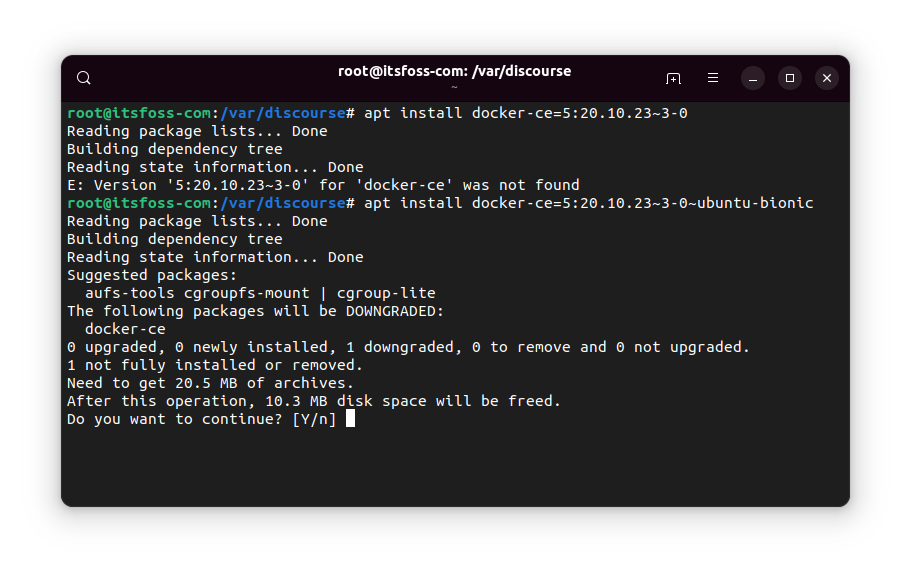
You’ll see a warning about downgrading the package, of course.
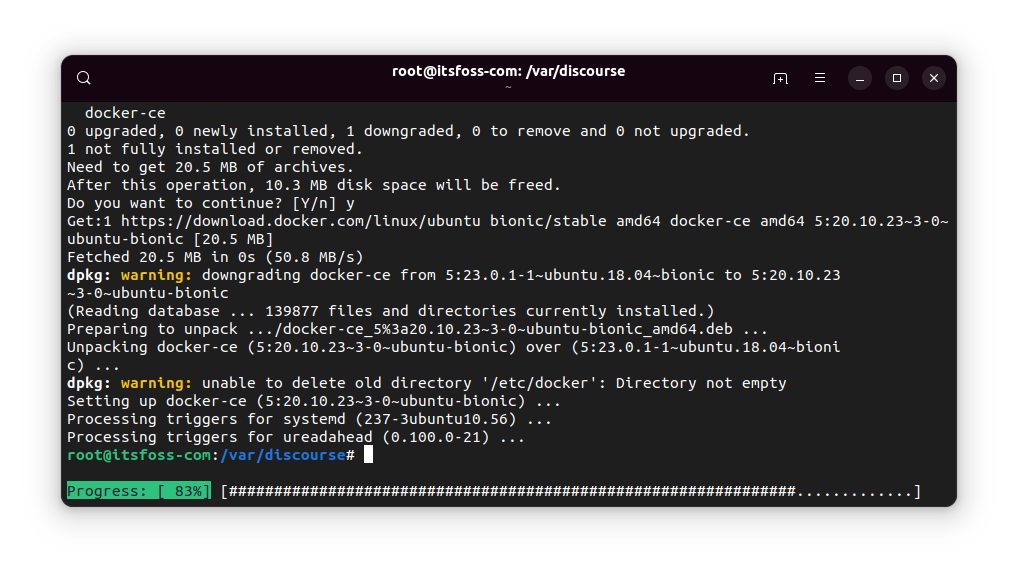
But once the process completes, your package would have been downgraded to the given older version.
So, hold it, maybe?
So, you just learned to downgrade apt packages. But if you don’t pay attention, the package will be upgraded again with the next system update.
Don’t want that? You can prevent a package from being updated. Use the apt-mark command like this:
sudo apt-mark hold package_nameWant more details? Check out this article.
How to Prevent a Package From Being Updated in Ubuntu and Debian-based Linux Distributions
Brief: Quick tutorial to show you how to prevent certain packages from being updated in Ubuntu and Debian based Linux distributions. When you update your Ubuntu system, all the applications, packages are updated at once. This is of course very convenient as you don’t have to worry about up…

I hope this quick tip helps you with downgrading the apt packages when the need arises. Let me know if you have questions or suggestions.
