How to Create and Extract RAR Files in Linux
RAR files, a common compressed file format, are widely used to store and share large amounts of data efficiently. While Linux natively supports various compression formats like ZIP and TAR.
RAR is the most popular tool for creating and extracting compressed archive (.rar) files. When we download an archive file from the web, we require a rar tool to extract them.
RAR is available freely under Windows operating systems to handle compressed files, but unfortunately, the rar tool isn’t pre-installed under Linux systems.
In this article, we’ll guide you through the process of installing unrar and rar command-line tools to open, extract, uncompress, or unrar and create an archive file on a Linux system.
Install rar and unrar on Linux
To work with RAR files on Linux, you’ll need the rar and unrar command-line utilities, which allow you to create and extract content from RAR archives.
To install rar and unrar, open a terminal and use the default package manager specific to your Linux distribution.
For example, on Debian and Ubuntu-based distributions, you can easily install the rar and unrar packages using the apt-get or apt program as shown.
$ sudo apt-get install rar unrar Or $ sudo apt install rar unrar
If you are using RHEL-based distributions, you can use the dnf command or yum command to install it.
------------ On Fedora Linux ------------ $ sudo dnf install rar unrar ------------ On RHEL-based Linux ------------ $ sudo yum install epel-release $ sudo yum install rar unrar
On other popular Linux distributions, you can install it using your default package manager as shown.
$ sudo emerge -a rar unrar [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add rar unrar [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S rar unrar [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install rar unrar [On OpenSUSE]
If your distribution does not offer rar and unrar packages, you need to download the latest unrar/rar file and install it using the following commands.
--------------- On 64-bit --------------- # cd /tmp # wget https://www.rarlab.com/rar/rarlinux-x64-700b2.tar.gz # tar -zxvf rarlinux-x64-700b2.tar.gz # cd rar # sudo cp -v rar unrar /usr/local/bin/ --------------- On 32-bit --------------- # cd /tmp # wget https://www.rarlab.com/rar/rarlinux-x32-700b2.tar.gz # tar -zxvf rarlinux-x32-700b2.tar.gz # cd rar # sudo cp -v rar unrar /usr/local/bin/
How to Create RAR File in Linux
To create an RAR archive file in Linux, run the following command with a option, which will create an archive file for a tecmint directory.
$ rar a tecmint.rar tecmint
How to Extract RAR Files in Linux
Once you have unrar installed, you can easily open or extract the contents of a RAR file in the current working directory by using the following command with the e option.
$ unrar e tecmint.rar
How to Extract RAR File to a Specific Directory
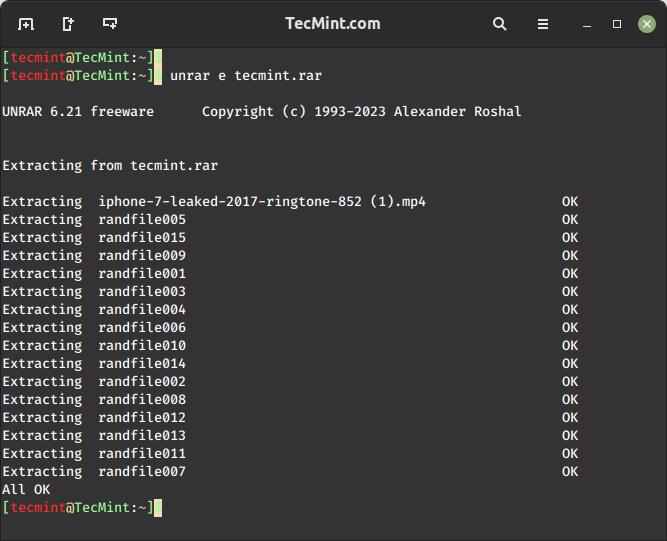
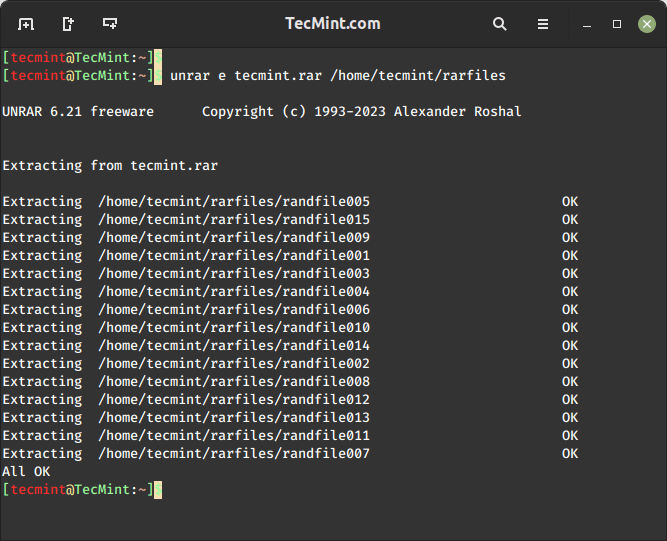
To open/extract a RAR file in a specific path or destination directory, use the e option, it will extract all the files in the specified destination directory.
$ unrar e tecmint.rar /home/tecmint/rarfiles
How to Extract RAR File with Directory Structure
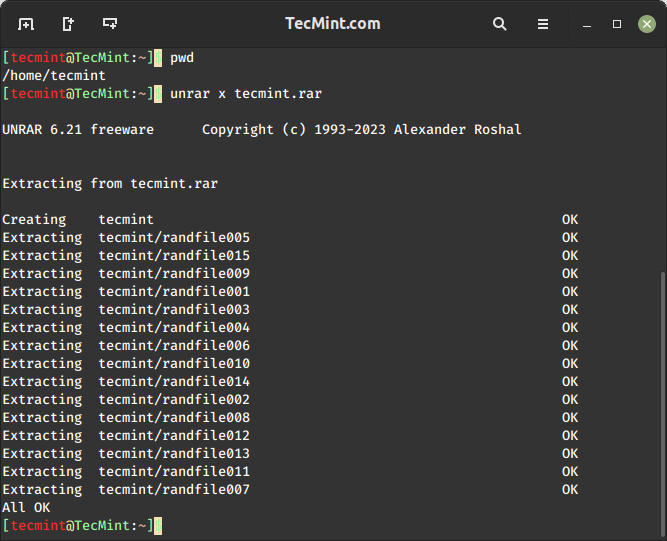
To open/extract an RAR file with its original directory structure, just issue the below command with the x option, which will extract according to their folder structure see below the output of the command.
$ unrar x tecmint.rar
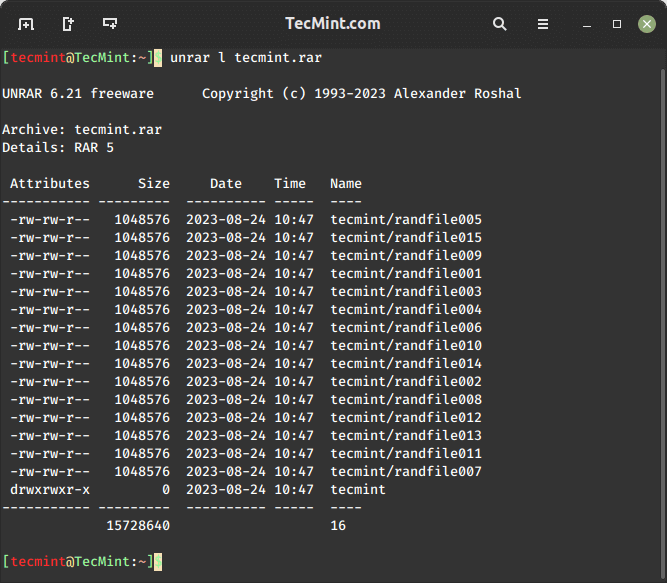
How to List RAR Files in Linux
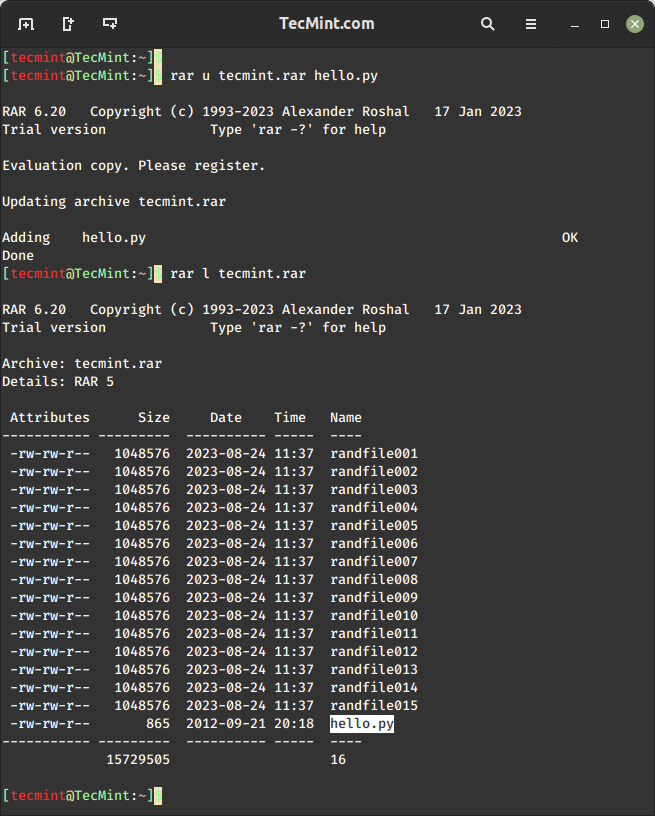
To list the contents of an RAR file in Linux, you can use the unrar l command, which will display the list of files with their sizes, dates, times, and permissions.
$ unrar l tecmint.rar
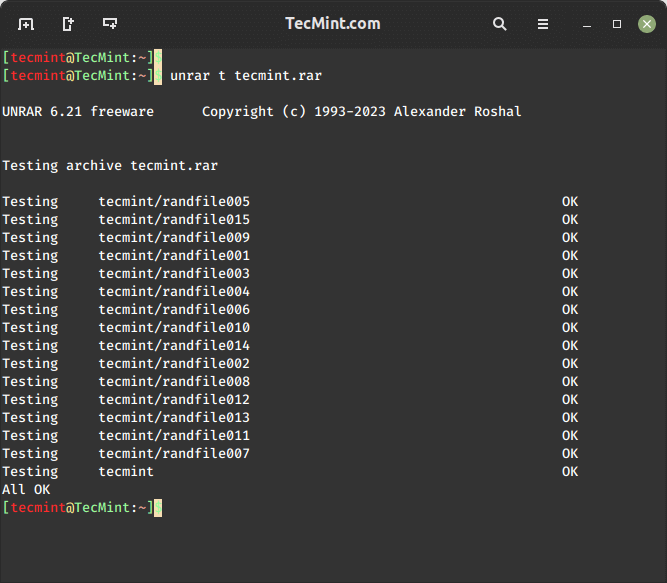
How to Check Integrity of RAR File in Linux
To check the integrity of an RAR archive file, you can use the unrar t command, which will perform a complete integrity check for each file for errors and displays the status of the file.
$ unrar t tecmint.rar
The unrar command only extracts, lists, or tests archive files. It has no option for creating RAR files under Linux. So, here we need to install the RAR command-line utility to create archive files.
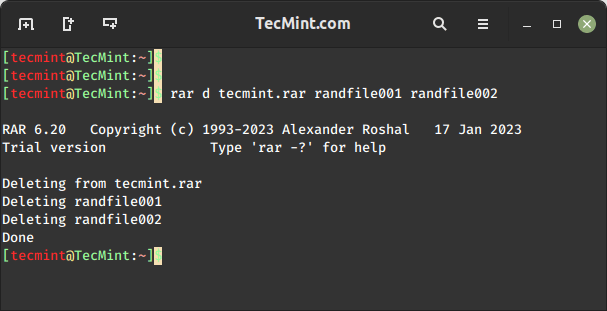
How to Delete Files in RAR Archive
The rar d command is used to delete files from an existing RAR archive in Linux. The d option directly modifies the existing RAR archive by removing the specified files.
$ rar d tecmint.rar randfile001 randfile002
In the above command, the randfile001 and randfile002 files will be deleted from the tecmint.rar RAR archive.
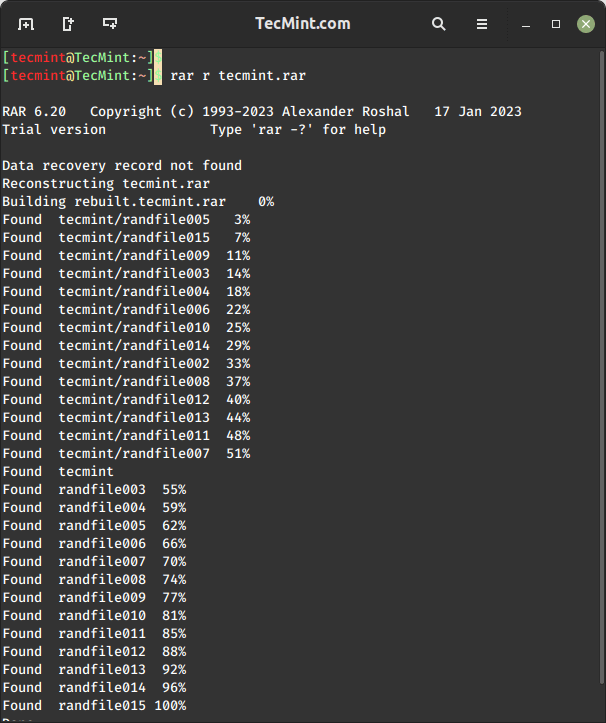
How to Repair RAR Files in Linux
The rar r command is used to repair and recover data from damaged or corrupted RAR archives in Linux.
$ rar r tecmint.rar
How to Add Files to RAR Archive
To update or add files to the existing archive file, use the rar u command, which allows you to add files to an existing RAR archive or update files within the archive.
$ rar u tecmint.rar hello.py
Now, verify that the file tecmint.sql is added to the archive file.
$ rar l tecmint.rar
How to Set Password to RAR File
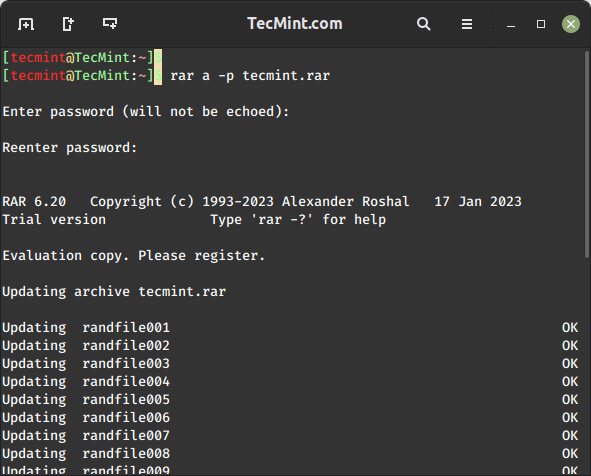
This is a very interesting feature of the rar tool, which allows us to set a password to the RAR archive file using the following command.
$ rar a -p tecmint.rar
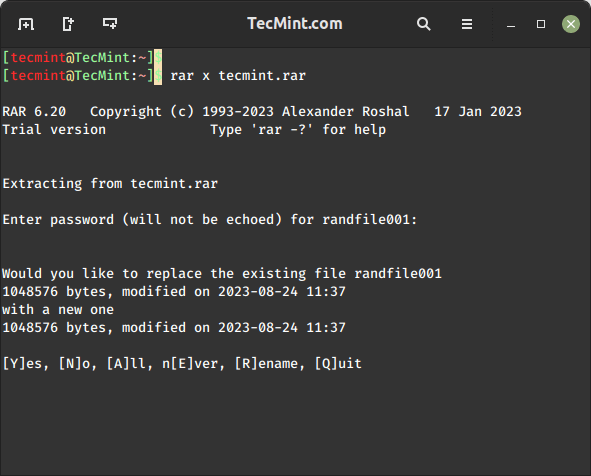
Now verify it by extracting the archive file and see whether it will prompt us to enter the password that we have set above.
$ rar x tecmint.rar
How to Lock RAR File
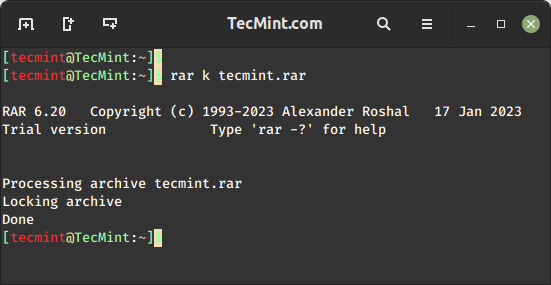
The rar k command is used to lock an existing RAR archive file, which is useful if you want to prevent further modifications to the archive.
$ rar k tecmint.rar
How to Split a RAR Archive
To split a RAR archive into 50MB parts or segments, use the following command with the -v50M option, which will split RAR file into four parts.
rar a -v50M archive_name.part.rar file1 file2 directory
Make sure to replace “archive_name.part.rar” with your desired archive name and size with the desired size (e.g., 50M or 100M). Include the files or directories you want to compress.
Conclusion
For more RAR and Unrar options and usage, run the following command it will display a list of options with their description.
$ man unrar $ man rar
We have presented almost all the options above for rar and unrar commands with their examples. If you feel that we’ve missed anything in this list and you would like us to add, please update us using the comment form below.